Vitamin D
23.08.2024
Vitamin D in Health and Well-being
Vitamin D, often referred to as the "sunshine vitamin," plays a crucial role in maintaining various aspects of our health. Unlike other vitamins, vitamin D is unique because our bodies can synthesize it when our skin is exposed to sunlight. This article delves into the origins of vitamin D, its chemical composition, how it affects our health, and the best ways to obtain it naturally. Additionally, we will explore in-depth studies on the importance of vitamin D, provide findings from scientific research, and introduce Coral Club D-Spray 2000—a leader in the vitamin industry.
What is Vitamin D?
Vitamin D is a fat-soluble vitamin that is essential for maintaining the health of bones and teeth, supporting the immune system, brain, and nervous system, and regulating insulin levels, among other functions. There are two main forms of vitamin D: D2 (ergocalciferol) and D3 (cholecalciferol). While both forms can increase vitamin D levels in the blood, D3 is more potent and has a longer duration of action in the body.
Chemical Structure and Types of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is part of a family of compounds that include vitamins D1, D2, D3, D4, and D5. However, the most biologically significant forms are vitamin D2 and D3. Vitamin D3 is synthesized in the skin when it is exposed to ultraviolet B (UVB) rays from the sun, while D2 is obtained from plant sources and fortified foods. Both forms are converted in the liver to 25-hydroxyvitamin D, the main circulating form of vitamin D, which is then converted in the kidneys to the active form, calcitriol.
The Origins of Vitamin D
Vitamin D has an evolutionary background tied to the need for humans and other animals to maintain adequate levels of calcium and phosphorus in the body. As life on Earth evolved, so did the mechanisms for producing and utilizing vitamin D. Early humans who lived near the equator had abundant exposure to sunlight, which facilitated the natural production of vitamin D. As humans migrated to higher latitudes with less sunlight, the ability to store and utilize vitamin D became crucial for survival.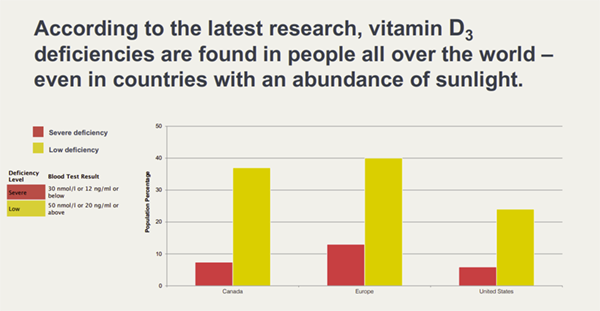
The Evolutionary Background of Vitamin D Synthesis
The ability to synthesize vitamin D in the skin was a critical adaptation that allowed early humans to thrive in various environments. This synthesis is a complex process that begins when UVB radiation from the sun converts 7-dehydrocholesterol, a compound in the skin, into previtamin D3. This substance is then converted into vitamin D3 through a heat-dependent process.
The Health Benefits of Vitamin D
Vitamin D is involved in numerous bodily functions, and its deficiency has been linked to a variety of health issues. Here, we will explore some of the key health benefits of vitamin D.
Bone Health and Calcium Regulation
One of the most well-known roles of vitamin D is in maintaining bone health. Vitamin D facilitates the absorption of calcium and phosphorus from the gut, which are critical for the formation and maintenance of strong bones. A deficiency in vitamin D can lead to bone diseases such as rickets in children and osteomalacia or osteoporosis in adults. These conditions result in soft, weak bones that are prone to fractures.
Immune System Support
Vitamin D plays a significant role in modulating the immune system. It enhances the pathogen-fighting effects of monocytes and macrophages—white blood cells that are important parts of your immune defense—and decreases inflammation. Studies have shown that individuals with adequate levels of vitamin D are less likely to develop autoimmune diseases and infections, such as respiratory tract infections and the flu.
Mental Health and Mood Regulation
Emerging research suggests that vitamin D is also important for mental health. Low levels of vitamin D have been associated with an increased risk of depression, anxiety, and other mood disorders. The exact mechanisms are still being studied, but it is believed that vitamin D affects the production of neurotransmitters such as serotonin, which are involved in mood regulation.
Cardiovascular Health
Vitamin D has been shown to have several effects on cardiovascular health. It may help reduce the risk of hypertension (high blood pressure), heart attack, and stroke. Vitamin D is thought to exert these effects by influencing the renin-angiotensin system (which regulates blood pressure) and improving the function of the endothelium (the inner lining of blood vessels).
Reducing the Risk of Chronic Diseases
Beyond bone health, vitamin D is implicated in the prevention of chronic diseases such as type 2 diabetes, certain cancers, and autoimmune conditions. For instance, studies have shown that adequate levels of vitamin D may reduce the risk of developing type 2 diabetes by improving insulin sensitivity and regulating blood sugar levels.
How to Get Vitamin D Naturally
Obtaining enough vitamin D is essential for health, and there are several ways to achieve this. The two primary sources of vitamin D are sunlight and dietary intake.
Sunlight: The Primary Source

The most natural way to get vitamin D is through exposure to sunlight. When your skin is exposed to UVB rays, it produces vitamin D3. Factors such as geographic location, time of year, skin pigmentation, and sunscreen use can affect how much vitamin D your body produces from sunlight. For example, people living closer to the equator or in sunnier climates can produce more vitamin D year-round compared to those living at higher latitudes.
Dietary Sources of Vitamin D
While sunlight is the primary source, vitamin D can also be obtained from certain foods. Natural sources of vitamin D include fatty fish (such as salmon, mackerel, and sardines), egg yolks, and liver. Additionally, many foods are fortified with vitamin D, including milk, orange juice, and cereals. However, it can be challenging to get enough vitamin D from food alone, which is why supplementation is often recommended, especially in regions with limited sunlight.
Factors Affecting Vitamin D Synthesis
Several factors can affect the body’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight. These include:
- Skin Pigmentation: Melanin, the pigment that gives skin its color, reduces the skin’s ability to produce vitamin D from sunlight. People with darker skin need more sun exposure to produce the same amount of vitamin D as those with lighter skin.
- Age: As people age, their skin’s ability to produce vitamin D decreases.
- Sunscreen Use: While sunscreen is important for protecting the skin from harmful UV rays, it can also block the production of vitamin D.
- Geographic Location and Season: People living at higher latitudes or in regions with long winters may not get enough sunlight for adequate vitamin D production, especially during the winter months.
Vitamin D is a vital nutrient with far-reaching effects on human health. From supporting bone health and immune function to protecting against chronic diseases, vitamin D is essential for maintaining overall well-being. While sunlight and diet are natural sources of vitamin D, supplementation is often necessary to ensure adequate levels, especially in regions with limited sun exposure. Coral Club’s D-Spray 2000 supplements offer a reliable and effective way to maintain optimal vitamin D levels, helping individuals achieve better health and vitality. As a leader in the vitamin industry, Coral Club continues to provide high-quality, research-backed products that meet the needs of health-conscious consumers worldwide.
In-Depth Study of Vitamin D
To fully appreciate the importance of vitamin D in health, it’s essential to examine the extensive body of scientific evidence and research findings. Here are some key case studies and clinical trials that highlight the benefits of vitamin D supplementation:
-
Bone Density in Postmenopausal Women:
- Study: Published in the Journal of Bone and Mineral Research.
- Focus: Investigated the effects of high-dose vitamin D supplementation on bone density.
- Findings: The study found that women who received high doses of vitamin D showed significant improvements in bone density, reducing their risk of fractures and osteoporosis.
- Implication: This research underscores the importance of vitamin D for bone health, particularly in populations at higher risk for bone density loss, such as postmenopausal women.
-
Influenza Prevention in Schoolchildren:
- Study: Published in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition.
- Focus: Examined the impact of vitamin D supplementation on the incidence of influenza in school-aged children.
- Findings: Children who received vitamin D supplements had a lower incidence of influenza compared to those who did not, suggesting that vitamin D plays a role in bolstering immune defenses against viral infections.
- Implication: This study highlights vitamin D’s potential in preventing respiratory infections, particularly in vulnerable populations such as children.
-
Cardiovascular Health:
- Study: Published in Circulation Research.
- Focus: Explored the relationship between vitamin D levels and cardiovascular health outcomes.
- Findings: Adequate vitamin D levels were associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular events, including heart attacks and strokes. Vitamin D was found to have a positive effect on blood pressure regulation and endothelial function.
- Implication: These findings suggest that maintaining sufficient vitamin D levels can contribute to better cardiovascular health, potentially reducing the burden of heart disease.
-
Vitamin D and Type 2 Diabetes Prevention:
- Study: Conducted by researchers at the Diabetes Research Institute.
- Focus: Assessed the impact of vitamin D supplementation on insulin sensitivity and blood sugar control in individuals at risk for type 2 diabetes.
- Findings: Participants who took vitamin D supplements demonstrated improved insulin sensitivity and better blood sugar control, indicating a reduced risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
- Implication: This study emphasizes the potential role of vitamin D in preventing metabolic disorders, particularly type 2 diabetes.
-
Mental Health and Mood Disorders:
- Study: Published in the Journal of Affective Disorders.
- Focus: Investigated the effects of vitamin D supplementation on symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Findings: Individuals with low vitamin D levels who received supplements reported significant improvements in mood and a reduction in symptoms of depression and anxiety.
- Implication: These results suggest that vitamin D may play a therapeutic role in managing mood disorders, potentially offering a natural adjunct to traditional treatments for depression and anxiety.
-
Cancer Prevention:
- Study: Published in The Lancet Oncology.
- Focus: Looked into the potential protective effects of vitamin D against certain types of cancer, including breast, colon, and prostate cancer.
- Findings: Higher levels of vitamin D were associated with a lower risk of developing certain cancers, possibly due to its role in cell growth regulation and immune function.
- Implication: This study supports the hypothesis that adequate vitamin D levels could reduce the risk of some cancers, highlighting its importance in long-term health maintenance.
-
Vitamin D Deficiency and Global Health:
- Study: Featured in Nature Reviews Endocrinology.
- Focus: Provided an overview of global vitamin D deficiency rates and the associated health impacts.
- Findings: The study revealed widespread vitamin D deficiency across various populations, even in regions with abundant sunlight, linking deficiency to increased risks of multiple chronic diseases.
- Implication: These findings emphasize the need for global public health initiatives to address vitamin D deficiency, particularly through supplementation and education on safe sun exposure.
These studies collectively highlight the critical role that vitamin D plays in various aspects of health, from bone density and immune function to cardiovascular health and chronic disease prevention. The consistent findings across different populations and health outcomes underscore the necessity of maintaining adequate vitamin D levels through a combination of sunlight exposure, diet, and supplementation.
Coral Club D-Spray 2000: The Leader in Vitamin D Supplements

Coral Club has established itself as a leader in the vitamin industry, particularly with its high-quality vitamin D products. Coral Club’s D-Spray 2000 supplements are formulated to provide optimal bioavailability and effectiveness, ensuring that users receive the full benefits of this essential nutrient.
The Quality and Purity of Coral Club D-Spray 2000
Coral Club’s D-Spray 2000 supplements are made from the highest quality ingredients, ensuring purity and potency. The company uses advanced manufacturing processes to produce vitamin D3, the most effective form of vitamin D, ensuring that the product is easily absorbed and utilized by the body. Additionally, Coral Club’s commitment to quality means that their supplements are free from artificial additives, preservatives, and allergens, making them suitable for a wide range of individuals.
The Benefits of Choosing Coral Club D-Spray 2000
Choosing Coral Club D-Spray 2000 offers several advantages:
- High Bioavailability: Coral Club’s D-Spray 2000 is designed for maximum absorption, ensuring that your body gets the most out of each dose.
- Supports Overall Health: Coral Club’s D-Spray 2000 supplements support bone health, immune function, cardiovascular health, and more.
- Trusted Brand: With years of experience in the supplement industry, Coral Club is a trusted name known for its commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
Customer Testimonials and Success Stories
Many individuals have experienced the benefits of Coral Club D-Spray 2000 firsthand. Customers report improvements in energy levels, immune function, mood, and overall well-being after incorporating Coral Club D-Spray 2000 into their daily routines. These testimonials highlight the effectiveness of Coral Club’s products in supporting health and wellness.
Resources:
Journal of Bone and Mineral Research
American Journal of Clinical Nutrition
Circulation Research
Diabetes Research Institute
Journal of Affective Disorders
The Lancet Oncology
Nature Reviews Endocrinology
How to purche D-Spray 2000 with 20% discount?
Coral Club membership program with a discount of 20% and more
When you register, you will be signed into Rut’s Kalnina’s structure, and she will be happy to answer all your questions as your consultant.
